Java Record as DTO in Spring Boot Application
In this section, we will show how we used Java Record as DTO in the Spring Boot application. The GitHub repository link is provided at the end of this tutorial. You can download the source code.
From Java 14 onwards, the record is a special type of class declaration aimed at reducing the boilerplate code.
Technologies used :
- Spring Boot 2.6.3
- Spring Data JPA
- Java 17
- H2 DB
- Maven 3+
Let's do it,
Final Project Directory
Maven[pom.xml]
A Project Object Model or POM is the fundamental unit of work in Maven. It is an XML file that contains information about the project and configuration details utilized by Maven to build the project.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.6.3</version> <relativePath /> </parent> <groupId>spring-boot-java-record</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-java-record</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-boot-java-record</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties> <java.version>17</java.version> </properties>
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa </artifactId> </dependency>
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
<!-- database --> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
</dependencies>
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin </artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
</project>Creating the Entity User
Records cannot be used as entities with JPA/Hibernate. JPA entities must have a no-args constructor, and must not be final, two requirements that the record will not support. More Information
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.GenerationType;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;
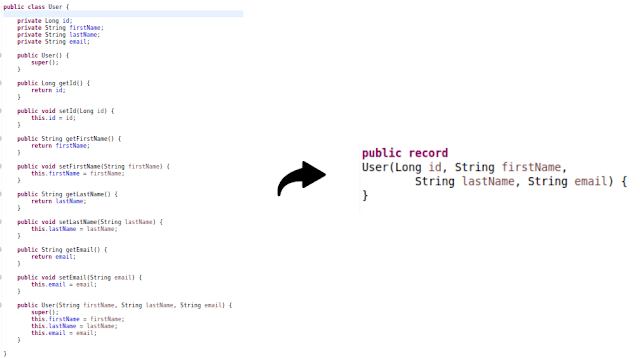
@Entity@Table(name = "user")public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private String email;
public User() { super(); }
public Long getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; }
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; }
public String getEmail() { return email; }
public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; }
public User(String firstName, String lastName, String email) { super(); this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; this.email = email; }
}Creating the User Repository
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.repsitory;
import java.util.List;import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.entity.User;
@Repositorypublic interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long> { List<User> findAll();} Creating the User Service
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.service;
import java.util.List;import java.util.Optional;import java.util.stream.Collectors;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.dto.User;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.repsitory.UserRepository;
@Servicepublic class UserService {
@Autowired UserRepository repsoitory ;
//User mapper public User mapUser(com.knf.dev.demo. springbootjavarecord. entity.User user) { User userDto = new User(user.getId(), user.getFirstName(), user.getLastName(), user.getEmail()); return userDto; }
public List<User> getAllUsers() { //Fetch all users List<com.knf.dev.demo. springbootjavarecord. entity.User> users = repsoitory.findAll();
//converting list of user entity to // list of user record using java stream return users.stream(). map(this::mapUser). collect(Collectors.toList()); }
public User getUserById(Long id) {
// Fetch user by id Optional<com.knf.dev.demo. springbootjavarecord. entity.User> user = repsoitory.findById(id);
// converting user entity to // user record return mapUser(user.get()); }}Java Record as DTO
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.dto;
public record User(Long id, String firstName, String lastName, String email) {}User Rest Controller
The @RestController annotation was introduced in Spring 4.0 to simplify the engendering of RESTful web services. It's a convenience annotation that combines @Controller and @ResponseBody. @RequestMapping annotation maps HTTP requests to handler methods of MVC and REST controllers.
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.controller;
import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.dto.User;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.service.UserService;
@RestController@RequestMapping("/api/v1/users")public class UserController {
@Autowired UserService userService;
@GetMapping public List<User> getAllUsers() { return userService.getAllUsers(); }
@GetMapping("/{id}") public User getUSerById(@PathVariable Long id) { return userService.getUserById(id); }}Spring Boot main driver
package com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord;
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.entity.User;import com.knf.dev.demo.springbootjavarecord.repsitory.UserRepository;
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootJavaRecordApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired UserRepository repository;
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication. run(SpringBootJavaRecordApplication.class, args); }
@Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { //Inserting dummy data User user1 = new User("dummy user", "dummy lastname", "dummy@gmail.com"); User user2 = new User("dummy user 2", "dummy lastname 2", "dummy@gmail2.com"); List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>(); users.add(user2); users.add(user1); repository.saveAll(users);
}}Local Setup and Run the application
Step1: Download or clone the source code from GitHub to the local machine - Click here
Step 2: mvn clean install
Step 3: Run the Spring Boot application - mvn spring-boot:run
Step1: Download or clone the source code from GitHub to the local machine - Click here
Step 2: mvn clean install
Step 3: Run the Spring Boot application - mvn spring-boot:run